Characteristics of coalbed methane accumulation in Bide-Santang syncline, western Guizhou and favorable sector
-
摘要:
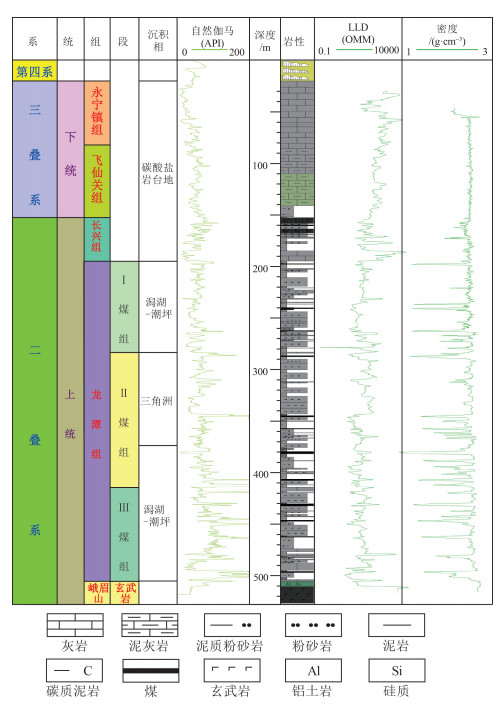
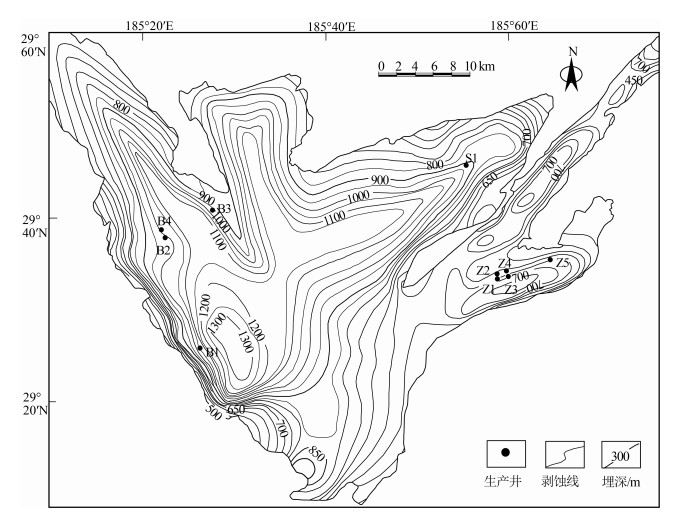
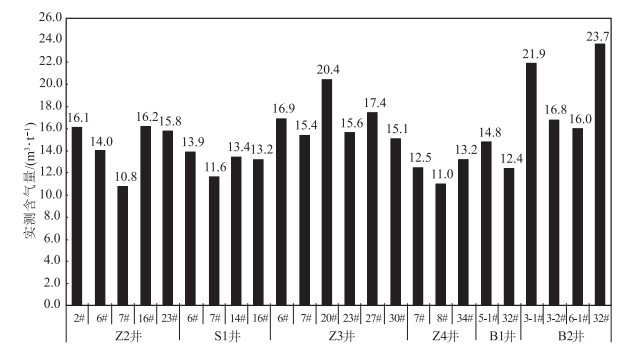
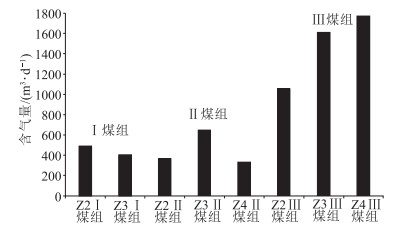
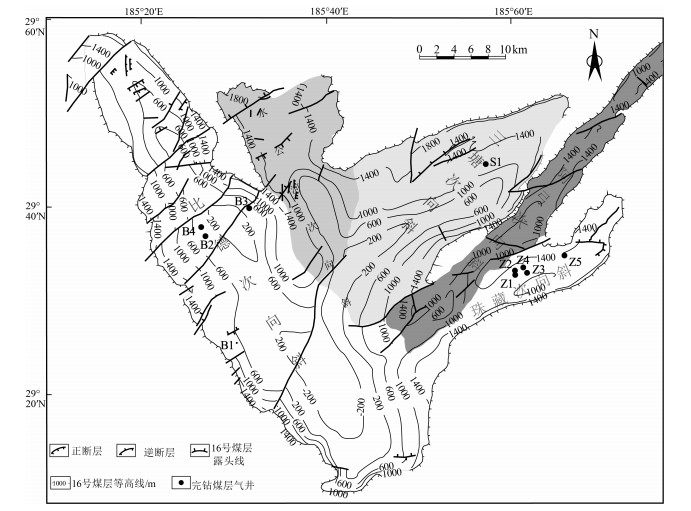
黔西比德-三塘向斜煤层气藏主要赋存于龙潭组Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ 3个煤组中,其中Ⅰ煤组6#和7#煤层、Ⅱ煤组16#和17#煤层、Ⅲ煤组20#、23#、27#、30#煤层分布稳定。煤层埋深受向斜构造控制明显,比德次向斜近轴部地区可达1500 m;煤岩以高变质的瘦煤、贫煤和无烟煤为主,最大镜质体反射率自西向东、由北到南逐渐增大;煤岩对甲烷吸附能力普遍较高(兰氏体积,18.32~39.32 m3/t),区域上受煤变质程度影响显著;原位埋深条件下,煤岩渗透率较低,煤层含气量整体较高,平均10~15.78 m3/t,含气饱和度普遍大于50%。结合该地区多层合采效果发现,比德次向斜埋深超过800 m的气井产气效果差,珠藏和三塘次向斜煤层气开发地质条件较好,其中珠藏向斜Ⅲ煤组4套主力煤层(煤层间距小于60 m)为潜在的高产优质储层。
Abstract:The coalbed methane(CBM) resource in the Bide-Santang synclineis hosted in three coal groups of the Longtan Formation, of which the coal seam No. 6 and 7 in group Ⅰ, the coal seam No. 16 and 17 in group Ⅱ, and the coal seam No. 20, 23, 27 and 30 in group Ⅲ are stably distributed. The seam depth is obviously controlled by syncline structure, reaching 1500m near the axis of Bide sub syncline. The coal seams are mainly high metamorphic lean coal, lean coal and anthracite, and the maximum vitrinite reflectance increases gradually from west to east and north to south. The methane adsorption capacity of coal is generally high(Langmuir volume, 18.32~39.32 m3/t), and is significantly affected by the coal metamorphism degree. Under the in-situ condition, the seams belong to typically low permeability reservoir, but with high gas content(average of 10~15.78 m3/t) and high gas saturation(generally >50%). Combined with the effect of multi-layer co-production in this area, it is found that the gas production effect of the gas wells with the inclined depth of more than 800m in Bide is poor, and the geological conditions of coal gas development in Zhizang and Santangxi syncline are relatively good. Among them, four sets of main coal seams(seam spacing < 60 m) of Ⅲ coal group in Zhizang syncline are potential high-yield and high-quality reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- multi seam /
- coalbed methane /
- reservoir conditions /
- favorable zone /
- Guizhou Province
-

-
表 1 比德-三塘向斜煤组划分
Table 1. The coal group division in the study area
煤组 煤田编号 主力煤层 煤层厚度/m Ⅰ煤组 2#→9#煤 6# 1.5~5.1(2.1) 7# 1.3~6.0(2.1) Ⅱ煤组 10#→19#煤 12# 0.8~1.4(0.96) 16# 0.9~4.1(2.04) 17# 0.8~1.42(1.17) Ⅲ煤组 20#→35#煤 20# 0.8~3.17(1.26) 23# 0.9~2.26(1.3) 27# 0.8~1.91(1.26) 30# 0.8~3.97(1.91) 表 2 部分典型参数井煤样等温吸附参数特征
Table 2. Isotherm adsorption parameters of typical wells
参数井 煤层 Ro/% VL/(m3·t-1) PL/MPa 比德向斜(B1井) 3-2# 1.93 19.92 1.78 5# 2.20 18.32 1.52 32# 2.12 22.47 2.43 三塘向斜(S1井) 6# 3.04 37.62 2.57 7# 3.14 37.20 2.41 14#上 3.25 33.72 2.75 14#下 3.36 37.94 2.45 珠藏向斜(Z2井) 2# 3.31 34.13 2.67 6# 3.44 35.41 2.75 7# 3.59 37.08 2.76 16# 4.30 34.61 2.55 23# 4.19 39.32 2.49 表 3 研究区各含煤构造单元煤层含气特征
Table 3. Coal seam gas content in each sub syncline
含煤次向斜 三塘 珠藏 水公河 比德 阿弓 < 300 m > 300 m < 200 m > 200 m 平均含气量/(m3·t-1) 6.75 11.2 8.07 15.79 15.78 12.14 10.48 钻孔测试层数 32 81 43 84 92 174 308 深度范围/m 102~287 300~740 24~191 200~749 90~824 63~926 38~694 平均深度/m 202.4 496.8 144.5 388.8 433 478 293 表 4 各含煤构造单元参数井煤层气含气饱和度和理论解吸压力
Table 4. Saturation and the theoretical desorption pressure of coals in each sub syncline
井号 构造单元 煤层编号 深度/m 兰氏体积/(m3·t-1) 兰氏压力/MPa 含气饱和度/% 解吸压力/MPa Z2 珠藏次向斜 6# 240.4 35.41 2.75 105 / 7# 262.4 37.08 2.76 68.6 1.13 16# 379.7 34.61 2.55 95.4 2.67 23# 430.5 39.32 2.49 79.2 1.92 S1 三塘次向斜 6# 614 37.62 2.57 65.1 2.1 7# 636.5 37.2 2.41 53.8 1.45 14# 697.7 37.94 2.45 62.6 2.04 16# 735.4 39.01 2.51 52.1 1.55 B1 比德次向斜 3-1# 639.1 13.91 0.81 / 6.6 5-1# 661.2 19.84 1.78 / 8.02 32# 898.4 22.27 2.43 72.9 8.64 33# 921.1 18.02 0.88 / 7.08 表 5 比德-三塘向斜煤层气试井及原位地应力测量参数
Table 5. Parameters of well testing and in-situ stress measurement in Bide-Santang syncline
井号 煤层 深度/m 储层压力/MPa 渗透率/mD 破裂压力/MPa 闭合压力/MPa Z2井 16# 380.95 2.95 0.0179 10.80 8.02 23# 431.38 3.04 0.0002 17.49 15.59 S1井 16# 736.98 6.86 0.0005 19.31 17.56 Z3井 27# 510.00 5.52 0.0744 18.84 12.01 B1井 32# 899.00 5.26 0.0001 17.00 15.15 B2井 6-1# 1027.00 9.14 0.0035 14.24 13.12 B3井 3-1# 1012.00 11.59 0.0025 15.71 15.21 W1井 2 # 520.17 5.12 0.1074 9.74 8.90 6-1+6-2 # 577.76 5.69 0.1682 12.81 11.75 W2井 2# 464.04 2.97 0.5002 8.77 8.09 5# 502.26 4.41 0.3228 9.28 8.75 6-1# 523.35 4.68 0.2999 9.73 9.31 -
[1] 桂宝林. 煤层气勘探目标评价方法——以滇东黔西地区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, (5): 6-7, 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200405011.htm
[2] 康高峰, 王辉, 王巨民, 等. 滇东北晚二叠世沉积体系与层序地层格架下的聚煤特征[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(1): 91-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.012 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090112&flag=1
[3] 徐宏杰, 桑树勋, 杨景芬, 等. 贵州省煤层气勘探开发现状与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2016, 44(2): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201602001.htm
[4] 徐宏杰. 贵州省薄-中厚煤层群煤层气开发地质理论与技术[D]. 中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2012.
[5] 刘贻军, 曾祥洲, 胡刚, 等. 贵州煤层气储层特征及勘探开发技术对策——以比德-三塘盆地为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2017, 45(1): 71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2017.01.014
[6] 熊斌, 刘晓, 马军, 等. 织金区块煤层气勘探潜力分析[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2012, (6): 72-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201206018.htm
[7] 孟美辰, 王运海, 袁航, 等. 织金区块煤层气井产气量影响因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(4): 187-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201904031.htm
[8] 窦新钊, 姜波, 秦勇, 等. 黔西地区构造演化及其对晚二叠世煤层的控制[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2012, 40(3): 109-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201203030.htm
[9] 窦新钊, 姜波, 张文永, 等. 黔西地区构造变形特征及其煤层气地质意义[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(8): 54-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.08.12
[10] 沈玉林, 秦勇, 郭英海, 等. 黔西上二叠统含煤层气系统特征及其沉积控制[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 18(3): 427-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201203004.htm
[11] 沈玉林, 秦勇, 郭英海, 等. 多层叠置独立含煤层气系统形成的沉积控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2012, 37(3): 573-579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201203021.htm
[12] Shen Y, Qin Y, Guo Y, et al. Characteristics and sedimentary control of a coalbed methane-bearing system in Lopingian(late Permian) coal-bearing strata of western Guizhou province[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2016, 33: 8-17.
[13] 杨兆彪. 多煤层叠置条件下的煤层气成藏作用[D]. 中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2011.
[14] 秦勇, 熊孟辉, 易同生, 等. 论多层叠置独立含煤层气系统——以贵州织金-纳雍煤田水公河向斜为例[J]. 地质论评, 2008, (1): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801009.htm
[15] 窦新钊. 黔西地区构造演化及其对煤层气成藏的控制[D]. 中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2012.
[16] 孟艳军, 汤达祯, 许浩, 等. 煤层气解吸阶段划分方法及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(5): 612-617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201405015.htm
[17] 张政, 秦勇, Wand G X, 等. 基于等温吸附实验的煤层气解吸阶段数值描述[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(8): 152-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201308010.htm
[18] 侯泉林, 雒毅, 韩雨贞, 李小诗. 煤的变形产气机理探讨[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(5): 715-722. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140513&flag=1
[19] Chen S, Tao S, Tang D, et al. Pore structure characterization of different rank coals using N2 and CO2 adsorption and its effect on CH4 adsorption capacity: a case in Panguan syncline, western Guizhou, China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31: 6034-6044. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00675
[20] Langmuir I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1918, 143: 1361-1403. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0020&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F01496390600851640&key=10.1021%2Fja02242a004
[21] 郭涛, 高小康, 孟贵希, 肖翠. 织金区块煤层气合采生产特征及开发策略[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2019, 47(6): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201906003.htm
[22] 许科, 崔彬. 等温吸附曲线在煤层气排采中的应用——以织金区块为例[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2015, 5(6): 73-75, 80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201506017.htm
[23] 杨兆彪, 张争光, 秦勇, 等. 多煤层条件下煤层气开发产层组合优化方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(2): 297-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201802013.htm
-



 下载:
下载: