A Cenozoic extensional angular unconformity on the northern margin of West Qinling Mountain and its geological significance
-
摘要:
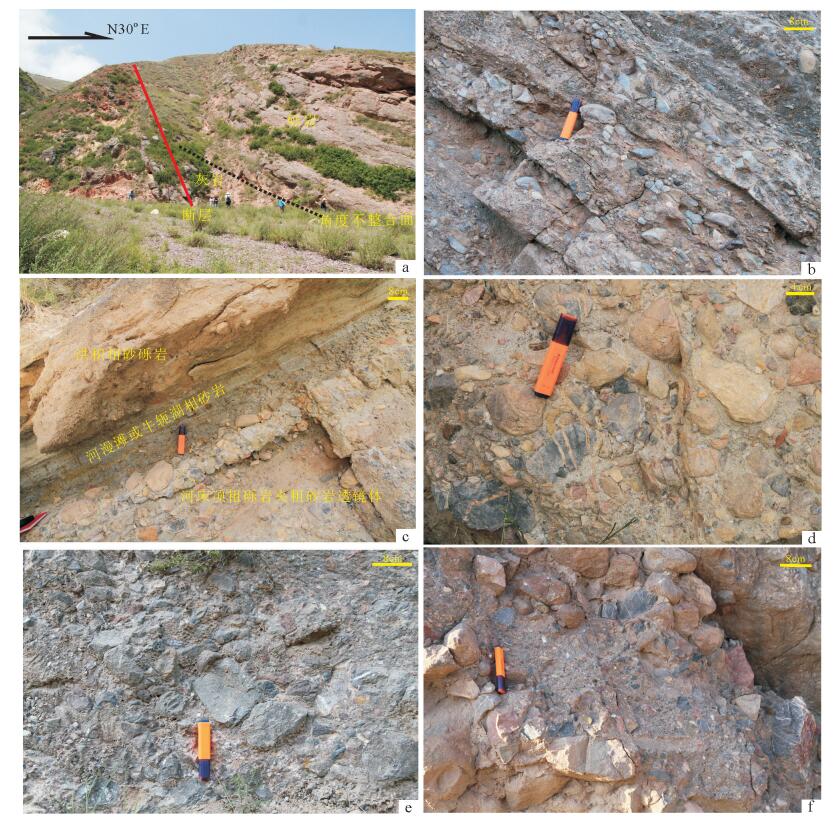
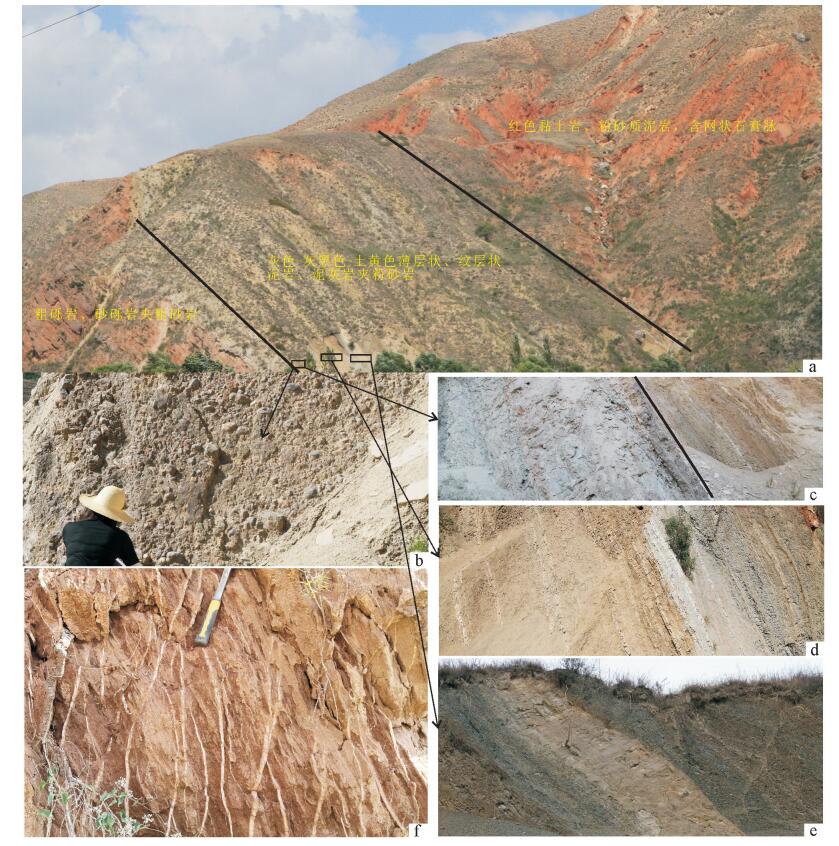
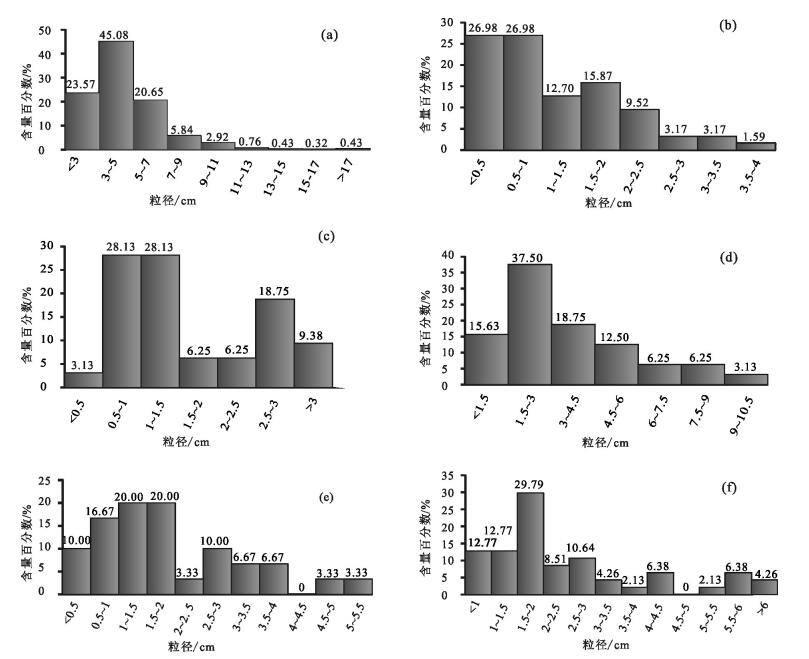
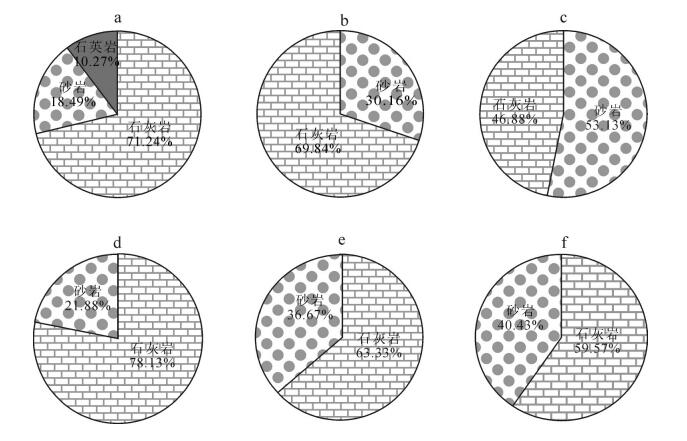
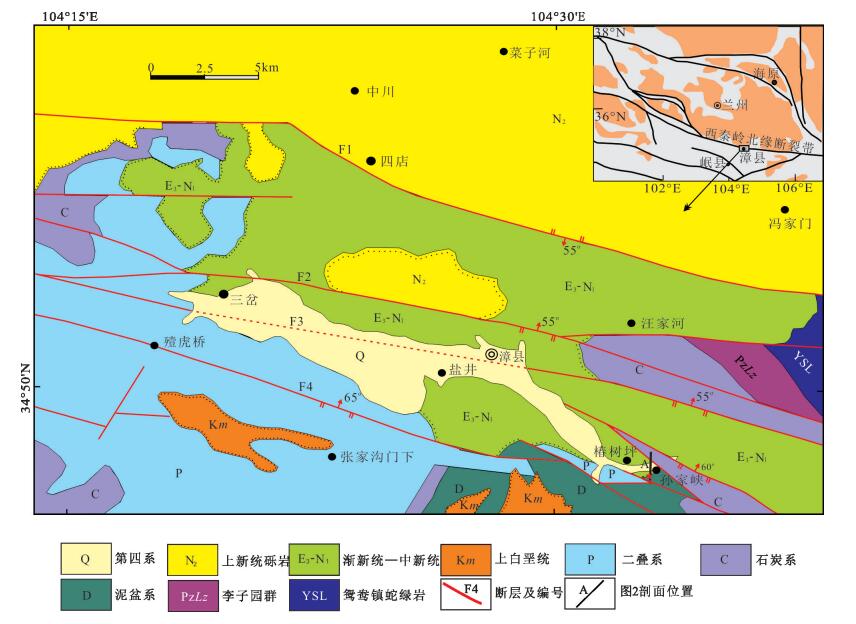
通过对西秦岭北缘漳县地区渐新统-中新统含盐红层地层与下伏造山带地层之间的角度不整合及其之上的砾岩、地层序列、沉积旋回等特征研究,提出了该角度不整合为伸展型角度不整合的认识。该伸展型角度不整合的存在指示了西秦岭北缘漳县渐新统-中新统含盐红层盆地具有伸展断陷盆地的属性,意味着在渐新世-中新世漳县含盐盆地形成和沉积充填时期,青藏高原东北缘(至少西秦岭北缘)一直处于伸展构造环境。这与印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞汇聚动力学作用向东北缘扩展形成的以挤压缩短和隆升为主的构造环境不协调,也就是说,青藏高原东北缘在渐新世-中新世可能尚未卷入现今青藏高原构造系统。
Abstract:Based upon detailed field observations and study for the angular unconformity between the Oligocene-Miocene salt-bearing red bed strata and its underlying orogenic strata in Zhangxian area of the northern margin of West Qinling Mountain and the characteristics of the conglomerates, stratigraphic sequence and sedimentary cycle of strata which cover the unconformity, the authors hold that this angular unconformity is an extensional angular unconformity developed under the crustal tensile tectonic setting. This extensional angular unconformity could provide the constraint on the tectonic attributes of the Oligocene-Miocene salt-bearing redbed basins in Zhangxian area of the northern margin of the West Qinling Mountain, that is, Zhangxian Oligocene-Miocene saltbearing red-bed basins is an extensional rift basin, which implies that the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau (at least the northern margin of West Qinling) might have been in an extensional tectonic environment in the Oligocene-Miocene period during the development and filling of the Zhangxian salt-bearing red-bed basin. This extensional tectonic environment was inconsistent with the crustal compression shortening and uplifting tectonic environment caused by spreading and extending of Cenozoic IndianEurasian collision to the northeast margin. It is therefore inferred that the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau should not be involved in the present Tibetan Plateau tectonic system during Oligocene-Miocene.
-

-
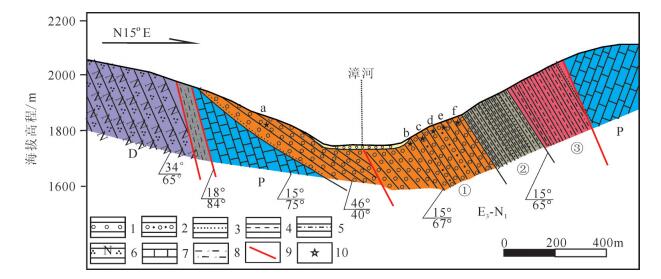
图 2 孙家峡地质剖面图(位置见图 1中A)
Figure 2.
-
[1] 中国地质调查局.中华人民共和国地质图(1:2500000)说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004.
[2] 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平.中国大陆构造中西秦岭-松潘大陆构造结[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):23-32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.004
[3] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 张万平, 等.青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013.
[4] 王修喜, 李吉均, 宋春晖, 等.青藏高原东北缘西秦岭新生代抬升——天水盆地碎屑颗粒磷灰石裂变径迹记录[J].沉积学报, 2006, 24(6):783-789. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2006.06.002
[5] 王志才, 张培震, 张广良, 等.西秦岭北缘构造带的新生代构造活动——兼论青藏高原东北缘形成过程的指示意义[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):119-135. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.010
[6] 张军.陇中盆地秦安-天水地区新近纪沉积物成因与环境变化[D].兰州大学博士学位论文, 2008.
[7] 张勇.陇西盆地东南隅新近纪沉积与环境演变[D].兰州大学博士学位论文, 2006.
[8] Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al. Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J]. Nature, 2002, 416:159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
[9] Wang Z C, Zhang P Z, Garmala N C, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and depositional history of the Miocene Wushan basin on the NE Tibetan Plateau, China:Implications for middle Miocene tectonics of the West Qinling fault zone[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 44:189-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.009
[10] Wang W T, Kirby E, Zhang P Z, et al. Tertiary basin evolution along the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Evidence for basin formation during Oligocene transtension[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2012, 125(3/4):377-400. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013GSAB..125..377W
[11] Wang X X, Li J J, Song C H, et al. Late Cenozoic orogenic history of Western Qinling inferred from sedimentation of Tianshui Basin, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2012, 101:1345-1356. doi: 10.1007/s00531-011-0724-5
[12] Wang X, Zattin M, Li J, et al. Eocene to Pliocene exhumation history of the Tianshui-Huicheng region determined by Apatite fission-track thermochronology:Implication for evolution of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau margin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42:97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.012
[13] 李吉均, 方晓敏, 马海洲, 等.晚新生代黄河上游地貌演化与青藏高原隆起[J].中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(4):316-322. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.04.005
[14] 方小敏, 徐先海, 宋春晖, 等.临夏盆地新生代沉积物高分辨率岩石磁学记录与亚洲内陆干旱化过程及原因[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27(6):989-1000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.06.014
[15] 袁道阳, 张培震, 方小敏, 等.青藏高原东北缘临夏盆地晚新生代构造变形及过程[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(1):243-250. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.023
[16] Zheng D W, Zhang P Z, Wan J L, et al. Late Cenozoic deformation subsequence in northeastern margin of Tibet-Detrital AFT records from Linxia Basin[J]. Science in China:Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(2):266-275. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zgkx-ed2003z2021.aspx
[17] Fang X M, Garzione C, Van der Voo R, et al. Flexural subsidence by 29Ma on the NE edge of Tibet from the magnetostratigraphy of Linxia Basin, China[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2003, 210:545-560. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00142-0
[18] Garzione C N, Ikari M J, Basu A R. Source of Oligocene to Pliocene sedimentary rocks in the Linxia basin in northeastern Tibet from Nd isotopes:Implications for tectonic forcing of climate[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2005, 117(9/10):1156-1166. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005GSAB..117.1156G
[19] Hough B G, Garzione C N, Wang Z C, et al. Stable isotope evidence for topographic growth and basin segmentation:Implications for the evolution of the NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(1/2):168-185. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2011GSAB..123..168H
[20] Liu S F, Zhang G W, Heller P L. Cenozoic basin development and its indication of plateau growth in the Xunhua-Guide district[J]. Science in China:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(Suppl 2):277-291. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/60111X/2007z2/1000887585.html
[21] 方小敏, 宋春晖, 戴霜, 等.青藏高原东北部阶段性变形隆升:西宁、贵德盆地高精度磁性地层和盆地演化记录[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(1):230-242. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.022
[22] 徐增连, 骆满生, 张克信, 等.青藏高原循化、临夏和贵德盆地新近纪沉积充填速率演化及其对构造隆升的响应[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(1):93-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.01.009 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130109&flag=1
[23] Fang X M, Yan M D, Van der Voo R, et al. Late Cenozoic deformation and uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from highresolution magnetostratigraphy of the Guide Basin, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 2005, 117(9/10):1208-1225. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_NSTL_QKJJ027179729.aspx
[24] 郭进京, 韩文峰, 胡晓隆, 等.西秦岭北缘新生代伸展断陷盆地确定及地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(5):230-244 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8281602
[25] 甘肃省地质矿产局.甘肃省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989.
[26] 郭进京, 韩文峰, 赵海涛, 等.西秦岭北缘漳县地区红层沉积地层格架及其地质意义[J].西北地质, 2016, 49(1):82-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.01.009
[27] 刘宝珺.沉积岩石学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1980
[28] 刘宝珺, 曾允孚.岩相古地理基础与工作方法[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985.
[29] 姜在兴.沉积学[M].北京:石油地质出版社, 2003.
[30] Friedman G M, Sanders J E. Principles of Sedimentology[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 1978.
[31] 郭进京, 吉夏, 赵海涛, 等.西秦岭北缘漳县韩家沟砾岩对青藏高原东北缘地壳隆升的约束[J].地质科学, 2017, 52(4):1011-1025 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201704001
[32] 万天丰.中国大地构造学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2011.
[33] 陈发景, 汪新文, 陈昭年.伸展断陷盆地分析[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004
[34] 陈发景, 汪新文, 陈昭年.前陆盆地分析[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:282.
[35] 李吉均, 方晓敏.青藏高原隆起与环境变化研究[J].科学通报, 1998, 43(15):1569-1574. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.15.001
[36] 葛肖虹, 任收麦, 马立祥, 等.青藏高原多期次隆升的环境效应[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(6):118-130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.015
[37] 王成善, 戴紧根, 刘志飞, 等.西藏高原与喜马拉雅的隆升历史和研究方法:回顾与进展[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(3):1-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.03.001
[38] 吴珍汉, 吴中海, 胡道功, 等.青藏高原新生代构造演化与隆升过程[M].北京:地质出版社, 2009.
[39] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等.造山的高原——青藏高原的地体拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007:1-458.
[40] Molnar P, England P, Martinod J. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian monsoon[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1993, 31(4):357-396. doi: 10.1029/93RG02030
[41] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28(1):211-280 doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
[42] Tapponnier P, Zhiqin X, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294(5547):1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
[43] Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, Van der Hilst R D. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2008, 321:1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371
[44] Wang C S, Dai J G, Zhao X X, et al. Outward-growth of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic:A review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 621:1-43 doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.01.036
[45] Li Y L, Wang C S, Dai J G, et al. Propagation of the deformation and growth of the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen:A review[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 2015, 143:36-61. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825215000100
[46] Yuan, D Y, Ge W P, Chen Z W, et al. The growth of northeastern Tibet and its relevance to large-scale continental geodynamics:A review of recent studies[J]. Tectonics, 2013, 32:1358-1370. doi: 10.1002/tect.20081
① 陕西地质局区测队.中华人民共和国1: 200000(I-48-IX陇西幅)地质图及说明书. 1970.
② 甘肃省地质调查院. 1: 250000(I48C002001岷县幅)区域地质调查报告. 2007.
-



 下载:
下载: