Determination of Cu, Pb and Zn in Sulfide Ores by Polarized Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
-
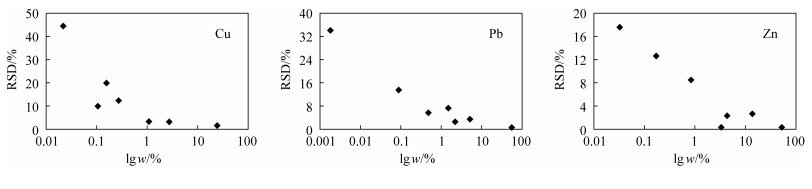
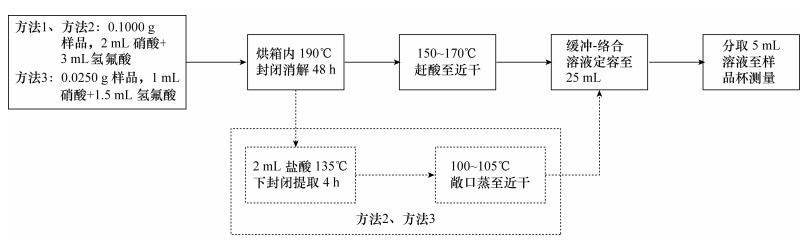
摘要: X射线荧光光谱法用于分析矿石主成分的常规制样方法有粉末压片法与玻璃熔融法,但分析硫含量高的地质样品时,前者存在矿物效应和粒度效应问题、后者可能腐蚀贵金属坩埚。为满足矿产勘查的需要,急需一种适应于硫化物矿石主成分分析的制样方法。本文建立了一种硝酸+氢氟酸封闭消解试样,标准溶液校准,偏振能量色散X射线荧光光谱(PE-EDXRF)同时测定硫化物样品中铜、铅、锌三种元素的分析方法。用GBW 07162~GBW 07168等7种矿石国家一级标准物质进行精密度和准确度实验。结果表明,当样品中铜、铅、锌元素含量大于1%时,几乎所有样品中的铜、铅、锌元素的精密度(RSD,n=6)优于5%,检测结果与标准值一致性良好。本方法通过样品消解、直接液体进样等技术的应用,消除了粒度效应和矿物效应等基体效应对分析结果的影响,解决了因缺乏基体匹配的标准物质而造成的含量校准的问题,使PE-EDXRF技术可以在硫化物矿石分析中得到比较方便的应用。这种分析方法为实验室矿石分析提供了新手段,也为野外现场PE-EDXRF分析高矿化度样品提供了新途径。Abstract: The traditional sample preparation methods are pressed powder pellets and glass melting to determine major components for sulfide ores by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. However, for high sulfur geological samples, the preparation method of pressed powder pellet has mineralogical effects and particle size effects, and the glass melting method has the disadvantage of being corrosive to precious metal crucibles. Development of a simple sample preparation method for principal components analysis is essential to meet the requirements for exploration of mineral deposits. In this paper a method is presented to determine Cu, Pb, Zn contained in sulfide ores. This method utilizes Polarized Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry (PE-EDXRF) along with nitric acid and fluoric acid digestion, and is calibrated by standard solution. The accuracy and precision of the method were examined by analyzing reference materials GBW 07162 to GBW 07168. The test results indicate that the relative standard deviations (RSD, n=6) of the most elemental components are less than 5%, when the concentrations of copper, zinc and lead are more than 1%. The results are in good agreement with certified values of reference materials. The impact of matrix effects such as particle size effect and mineral effect on analytical elements has been eliminated by digestion sample and direct solution inlet. The problem of calibrating concentrations that were short of standard materials has been solved with the matrix matching. The technology of PE-EDXRF provides a new means of ore analysis in the laboratory and a new technical support for PE-EDXRF field analysis for high sulfide samples.
-
Key words:
- sulfide ores /
- copper /
- lead /
- zinc /
- Polarized Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry /
- solution method /
- acid digestion
-

-
表 1 标准溶液中各元素的浓度
Table 1. Concentrations of the elements in calibration standard solution
样品编号 ρ/(μg·mL-1) Cu Pb Zn 标准溶液1 2000 1000 200 标准溶液2 1000 200 40 标准溶液3 200 40 2000 标准溶液4 40 2000 1000 标准溶液5 0 0 0 表 2 三种样品前处理方法结果比较
Table 2. Comparison of analytical results by three sample pretreatment methods
标准物质
编号元素 w/% 标准值 方法1 方法2 方法3 GBW 07163 Cu 1.05 1.05 1.16 1.02 Pb 2.17 2.17 2.45 2.17 Zn 4.26 4.28 4.42 4.10 GBW 07165 Cu 0.096 0.13 0.27 0.13 Pb 5.13 4.69 5.58 4.93 Zn 13.90 13.78 14.16 13.71 表 3 测量元素铜的准确度与精密度
Table 3. Accuracy and precision tests for Cu
标准物质
编号w(Cu)/% 标准偏差/% 标准值 测量值(n=6) GBW 07162 - - 0.035 GBW 07163 - - 0.037 GBW 07164 2.80±0.09 2.70±0.16 0.095 GBW 07165 0.096±0.007 0.102±0.016 0.010 GBW 07166 24.2±0.2 24.0±0.6 0.35 GBW 07167 0.028±0.007 0.021±0.016 0.0095 GBW 07168 0.138±0.008 0.157±0.051 0.031 注:“±”值为99%置信度下的不确定度。 表 4 测量元素铅的准确度与精密度
Table 4. Accuracy and precision tests for Pb
标准物质
编号w(Cu)/% 标准偏差/% 标准值 测量值(n=6) GBW 07162 0.43±0.02 0.48±0.05 0.028 GBW 07163 2.17±0.07 2.20±0.09 0.056 GBW 07164 0.056±0.005 0.088±0.019 0.012 GBW 07165 5.13±0.08 5.22±0.31 0.19 GBW 07166 0.04±0.005 0.002±0.001 0.0007 GBW 07167 57.1±0.3 56.4±0.4 0.26 GBW 07168 1.44±0.03 1.47±0.18 0.11 注:“±”值为99%置信度下的不确定度。 表 5 测量元素锌的准确度与精密度
Table 5. Accuracy and precision tests for Zn
标准物质
编号w(Cu)/% 标准偏差/% 标准值 测量值(n=6) GBW 07162 0.83±0.04 0.85±0.12 0.074 GBW 07163 4.26±0.15 4.23±0.17 0.10 GBW 07164 0.143±0.006 0.172±0.036 0.022 GBW 07165 13.9±0.2 14.0±0.6 0.37 GBW 07166 (0.057) 0.032±0.009 0.0057 GBW 07167 3.3±0.1 3.3±0.1 0.012 GBW 07168 52.7±0.3 52.2±0.4 0.21 注:括号内数据表示不符合标准值要求的参考值;“±”值为99%置信度下的不确定度。 -
[1] 李冰,周剑雄,詹秀春.无机多元素现代仪器分析技术[J].地质学报,2011,85(11): 1878-1916. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201111009.htm
[2] 马生凤,温宏利,马新荣,王蕾,巩爱华,曹亚平,屈文俊.四酸溶样-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定铁,铜,锌,铅等硫化物矿石中22个元素[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,2011,30(1): 65-72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201101010.htm
[3] 谢忠信.X射线光谱分析[M].北京:科学出版社,1982: 249.
[4] 特希昂R,克莱斯F.X射线荧光定量分析原理[M].北京:冶金部钢铁研究总院,1999: 106-109.
[5] 罗立强,詹秀春,李国会.X射线荧光光谱仪[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2008.
[6] 胥成民,刘邦杰.铁矿的X射线荧光光谱分析[J].理化检验(化学分册),1999,35(2): 61-62. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-SOEN200205002051.htm
[7] 李升,李锦光.X射线荧光光谱-玻璃熔融制样法分析铁矿中主成分和微量成分[J].光谱实验室,1999,18(3): 345-347. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GPSS903.032.htm
[8] 王莉莉,耿玉良,王松青.铁矿石的X射线荧光光谱分析[J].分析试验室,1988,7(8): 5. http://youxian.cnki.com.cn/yxdetail.aspx?filename=JSTB201708061&dbname=CJFDPREP
[9] 蒋薇.X射线荧光光谱法测定钒钛磁铁矿成分[J].光谱实验室,2005,22(5): 940-942.
[10] 张莉娟,徐铁民,李小莉,安树清,韩伟,张楠,刘义博.X射线荧光光谱法测定富含硫砷钒铁矿石中的主次量元素[J].岩矿测试,2011,30(6): 772-776. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201106028.htm
[11] 李国会.X射线荧光光谱法测定铬铁矿中主次量[J].岩矿测试,1999,18(2): 131-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS902.011.htm
[12] 王再田,牛素琴,邓虹.XRF光谱测定钨精矿WO3(%)简便方法[J].光谱学与光谱分析,1999,19(1): 93-94.
[13] 蒋薇,刘伟. X射线荧光光谱法测定锰矿石成分[J].冶金标准化与质量,2006,44(5): 10-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJBL200605002.htm
[14] 张耀奎,支河,肖海斌,左天明,徐义仁.X射线荧光光谱法测定锰矿石中主次成分[J].四川地质学报,2012,32(4): 503-505. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB201204034.htm
[15] Gyves J,李国会.X射线荧光谱法直接测定锌精矿中的锌铅铁和全硫[J].物探化探译丛,1990(5): 58-62.
[16] 赵耀,王再田.XRF熔融制样法测定铜精矿中的Cu,Fe,S,Pb,Zn,As,Bi,Mo[J].分析试验室,1999,18(1): 19-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY901.005.htm
[17] Potts P J, Webb P C, Watson J S. Silicate rock analysis by energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence using a cobalt anode X-ray tube. Part Ⅰ.Optimisation of excitation conditions for chromium, vanadium, barium and the major elements[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1986,1(6): 467-471. doi: 10.1039/ja9860100467
[18] Potts P J, Webb P C, Watson J S, Wright D W. Silicate rock analysis by energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence using a cobalt anode X-ray tube. Part 2. Practical application and routine performance in the determination of chromium, vanadium and barium[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1987,2(1): 67-72. doi: 10.1039/ja9870200067
[19] Potts P J, Webb P C, Watson J S.Energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence analysis of silicate rocks for major and trace elements[J]. X-Ray Spectrometry,1984,13(1): 2-15. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4539
[20] Margolin E M, Pronin Y I, Choporov D Y, Shil'nikov A M, Komyak N I, Goganov D A, Serebryakov A S, Fed'kov E A. Some experience in using the MECA-10-44(XR-500) X-ray fluorescence analyser for solving geological problems[J].X-Ray Spectrometry,1985,14(2): 56-61. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4539
[21] 樊兴涛,李迎春,王广,白金峰,姚文生,袁继海,詹秀春.车载台式能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪在地球化学勘查现场分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试,2011,30(2): 155-159. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201102008.htm
[22] 袁汉章,吴长存,卜赛斌,张虎云,许佩珍,武清富.铜矿选矿流程中铜、铁、硫、硅、铝、钼和钛的X射线荧光光谱直接测定[J].分析化学,1981,9(2): 146-152. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX198102004.htm
[23] 李晃,李莉. EDXRF测定铅烧结块的粒度效应[J].湖南有色金属,1994(10): 190. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYJ403.021.htm
[24] 徐君铎,方明渭,董克家.铅锌矿中铅,锌,铁,铜溶液法X荧光连测[J].上海有色金属,1980(Z1): 77-80. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHHA1980S1015.htm
[25] 符斌,方明渭,周杰,岳永平,李华昌,王红霞.用于X射线荧光光谱分析的凝胶制样法[J].冶金分析,2002,22(5): 6-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJFX200205002.htm
[26] Zhang G, Hu X, Ma H. A gel sample preparation method for the analysis of zinc concentrates by WD-XRF[J].Minerals Engineering, 2009,22(4): 348-351. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2008.10.001
[27] 张英,周长民.柠檬酸钠的特性与应用[J].辽宁化工,2007,36(5): 350-352. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNHG200705021.htm
[28] 符斌.常用化学手册[M].北京:地质出版社,1997: 461.
-



 下载:
下载: