Iron Recovery from Tailings of the Smelting Slag after Copper Flotation with Magnetic Separation-reverse Flotation
-
摘要:
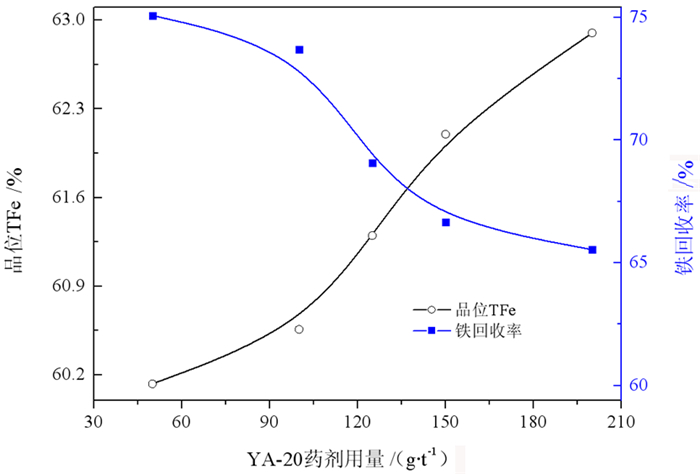
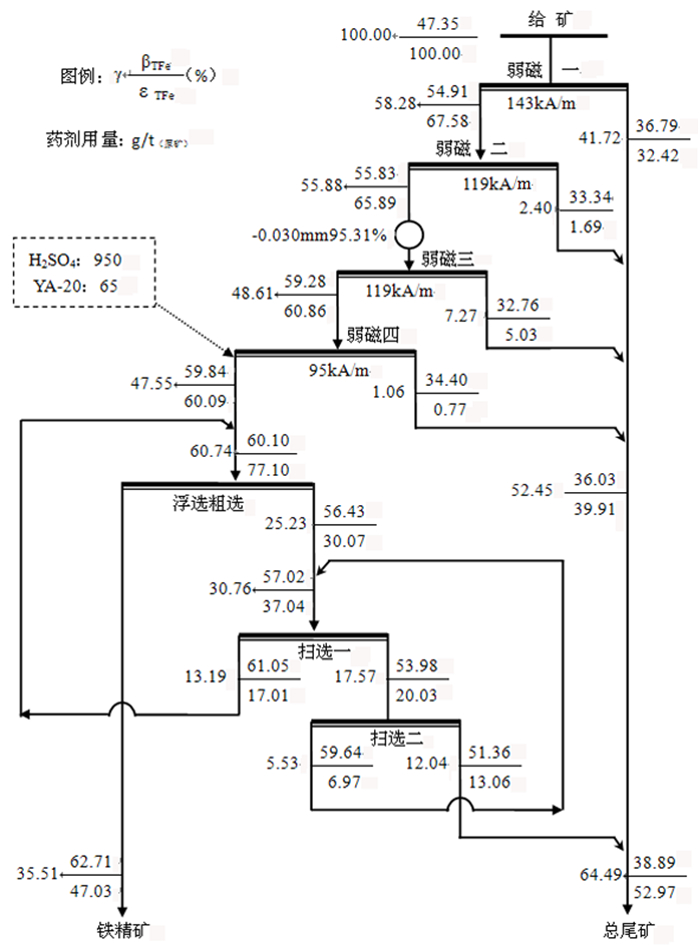
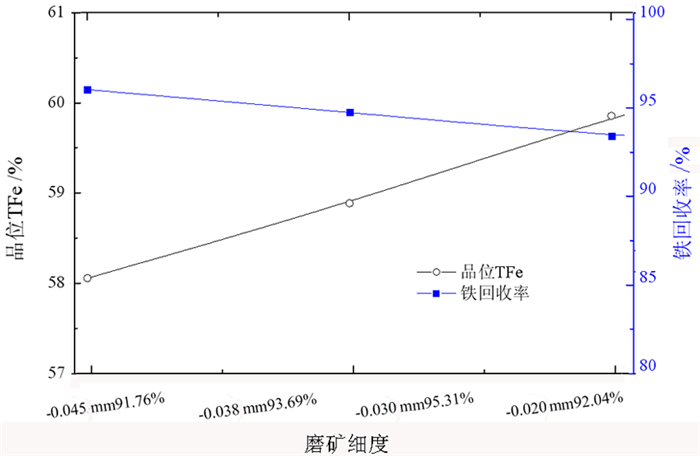
为了回收某铜冶炼渣中的铁, 在工艺矿物学研究基础上, 进行了磨矿—弱磁选—反浮选技术研究。研究结果表明, 样品中Fe含量高达47.14%, 主要赋存于磁铁矿和含铁硅酸盐中, 分布率分别为53.01%、44.38%。在磨矿细度-0.030 mm占95.31%时, 采用弱磁选—反浮选工艺, 可获得产率35.51%、TFe品位62.71%、铁回收率47.03%的铁精矿; 尾矿可作为水泥铁质调整料销售。最终实现铜渣中铁金属的综合回收及无尾排放。
Abstract:In order to recover iron from tailings of the smelting slag after copper flotation, the separation process of grinding- low magnetic separation-reverse flotation was carried out based on the process mineralogy research results. The results showed that the iron content in the sample was as high as 47.14%. The distribution rate of iron in the magnetite form and in the iron-containing silicate form were 53.01% and 44.38%, respectively. When the grinding fineness was 95.31%(-0.030 mm) and the the separation process of grinding- low magnetic separation-reverse flotation was carried out, the iron concentrate was obtained with yield of 35.51%, TFe grade of 62.71% and iron recovery of 47.03%. Tailings can be sold as iron conditioner for cement industry. Finally, the comprehensive recovery and tailless discharge of iron in the smelting slag would be realized.
-
Key words:
- copper smelting slag /
- beneficiation /
- magnetic separation /
- reverse flotation /
- comprehensive recovery
-

-
表 1 试样化学多元素分析结果
Table 1. Chemical multielement analysis of the sample
/% 组分 Fe FeO Fe2O3 Cu Pb Zn SiO2 Al2O3 含量 47.14 38.13 25.04 0.30 0.47 1.89 23.30 3.82 组分 CaO MgO K2O Na2O As S P 含量 2.63 1.14 0.83 0.31 0.052 0.23 0.06 表 2 试样铁物相分析结果
Table 2. Iron phase analysis results of the sample
/% 铁相 含量 分布率 金属铁 0.22 0.47 磁铁矿中铁 24.99 53.01 赤褐铁矿中铁 0.84 1.78 硫化物中铁 0.10 0.21 碳酸盐中铁 0.07 0.15 硅酸盐中铁 20.92 44.38 合计 47.14 100.00 表 3 试样中主要矿物含量分析结果
Table 3. Main mineral content in the sample
/% 矿物 磁铁矿 金属铁 赤(褐)铁矿 金属铜 斑铜矿 辉铜矿 方黄铜矿 赤铜铁矿 含量 36.35 0.22 1.20 0.01 0.19 0.09 0.08 0.11 矿物 砷铜矿 金属铅+方铅矿 金属锌+闪锌矿 铁橄榄石 玻璃体 石英 其他 含量 0.01 0.02 0.03 34.73 25.92 0.89 0.15 表 4 铜尾渣直接弱磁选场强试验结果
Table 4. Results of the direct low intensity magnetic separation of copper tailings
磁选场强 产品名称 产率/% TFe品位/% 铁回收率/% 粗选:0.18 T
精选:0.12 T精矿 53.65 55.90 63.73 中矿 2.33 34.12 1.69 尾矿 44.02 36.97 34.58 给矿 100.00 47.06 100.00 粗选:0.20T
精选:0.18 T精矿 55.88 55.83 65.89 中矿 2.40 33.40 1.69 尾矿 41.72 36.79 32.42 给矿 100.00 47.35 100.00 粗选:0.30T
精选:0.20 T精矿 55.97 55.64 66.05 中矿 2.51 33.61 1.79 尾矿 41.52 36.52 32.16 给矿 100.00 47.15 100.00 表 5 弱磁粗精矿中磁铁矿解离度分析结果
Table 5. Liberation analysis of magnetite in the coarse concentration after low intensity magnetic separation
/% 单体 连生体 >3/4 3/4~1/2 1/2~1/4 <1/4 57.6 21.3 12.7 6.0 2.4 表 6 二段弱磁选场强试验结果
Table 6. Results of two stage low magnetic field strength
磁选场强 产品名称 产率/% TFe品位/% 铁回收率/% 粗选:0.12 T
精选:0.10 T精矿 87.06 59.90 92.20 中矿 1.33 35.12 0.83 尾矿 11.61 33.97 6.97 给矿 100.00 56.56 100.00 粗选:0.15 T
精选:0.12 T精矿 88.01 59.84 93.03 中矿 1.53 34.53 0.93 尾矿 10.46 32.70 6.04 给矿 100.00 56.61 100.00 粗选:0.20 T
精选:0.18 T精矿 88.23 59.79 93.21 中矿 1.87 33.48 1.11 尾矿 9.90 32.52 5.68 给矿 100.00 56.60 100.00 表 7 铁精矿化学多元素分析结果
Table 7. Chemical multielement analysis of the iron concentrate
/% 组分 TFe FeO SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO MnO 含量 63.08 33.64 4.40 2.68 0.50 0.46 0.060 组分 K2O Na2O Cu Au/g/t Ag/g/t S P 含量 0.14 0.067 0.19 0.30 7.89 0.083 0.014 表 8 尾矿化学多元素分析结果
Table 8. Chemical multielement analysis of the tailings
/% 组分 TFe FeO SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO MnO 含量 39.78 42.65 32.79 3.02 3.41 1.72 0.12 组分 K2O Na2O Cu Au Ag S P 含量 0.91 0.32 0.52 0.59 7.64 0.27 0.084 注:Au、Ag单位为g/t。 -
[1] 邱廷省, 周丽萍, 李国栋. 铜冶炼渣直接还原焙烧-磁选回收铜, 铁试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(9): 6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202009030.htm
QIU T S, ZHOU L P, LI G D. Experimental of copper and iron recovery from copper smelting slag by direct reduction roasting and magnetic separation[J]. METAL MINE, 2020(9): 6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202009030.htm
[2] 曹志成, 孙体昌, 薛逊, 等无烟煤转底炉直接还原铜渣回收铁、锌研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2017, 37(2): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.02.019
CAO Z C, SUN T C, XUE X, et al. Recovery of iron and zinc from copper slag by rotary hearth furnace with anthracite as reductant[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2017, 37(2): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2017.02.019
[3] 代献仁, 林小凤, 袁启东, 等. 某铜冶炼渣中回收铜铁试验研究[J]. 冶金矿山与冶金设备, 2021, 37(7): 116-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202107030.htm
DAI X R, LIN X F, YUAN Q D, et al. Experimental study on recovery of copper and iron from copper smelting slag[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(7): 116-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202107030.htm
[4] 刘先阳, 李杰, 张琳, 等. 铜渣深度还原回收铁技术进展[J]. 现代化工, 2019, 39(3): 31-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDHG201903007.htm
LIU X Y, LI J, ZHANG L, et al. Technical progress in recovering iron from copper slag by deep reduction[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(3): 31-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDHG201903007.htm
[5] 刘宏图, 曹亦俊, 范桂侠. 铜冶炼渣综合回收利用进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(3): 34-42. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b07e2498-82ad-45a1-b82b-06813bd18f39
LIU H T, CAO Y J, FAN G X. Progress in comprehensive recovery and utilization of copper smelting slag[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021, 41(3): 34-42. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b07e2498-82ad-45a1-b82b-06813bd18f39
[6] 杨椿, 余洪. 从铜冶炼渣中回收铁的试验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2014(5): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL201405014.htm
YANG C, YU H. Experimental study of recovery of iron from copper smelting slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources. 2014(5): 55-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCZL201405014.htm
[7] 周中元. 铜冶炼渣综合回收研究[J]. 低碳世界, 2015(19): 153-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH202103005.htm
ZHOU Z Y. Comprehensive recovery of copper smelting slag[J]. Low Carbon World, 2015(19): 153-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCBH202103005.htm
[8] 朱茂兰, 熊家春, 胡志彪, 等. 铜冶炼渣选铜尾矿还原焙烧-磁选回收铁工艺研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2016(7): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201607004.htm
ZHU M L, XIONG J C, HU Z B, et al. Iron recovery from copper tailings of copper smelting slag with reduction roasting and magnetic separation[J]. Nonferrous Metals (extractive metallurgy), 2016(7): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201607004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: